Nitrogen-Fixing Edible Plants
Essential Nutrient!
Nitrogen is an element responsible for lush green plant growth, but most plants aren't able to use the nitrogen gas in Earth's atmosphere. Non-organic farmers and gardeners use chemical nitrogen fertilizer to keep crops thriving, but this synthetic fertilizer can pose a threat to the environment. It pollutes our waterways, threatening our drinking water supply, fish and other wildlife. Biological nitrogen fixation through plants helps crops flourish without introducing pollutants to the environment.
A Symbiotic Relationship Between Plants and Bacteria
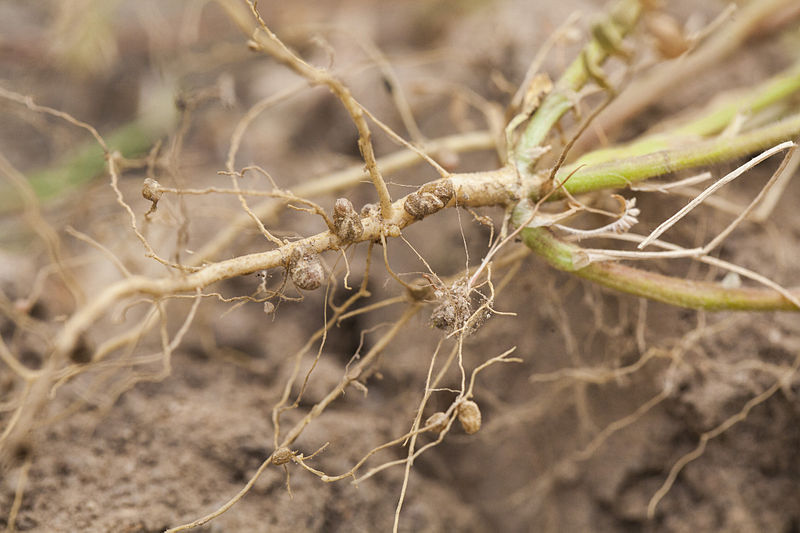
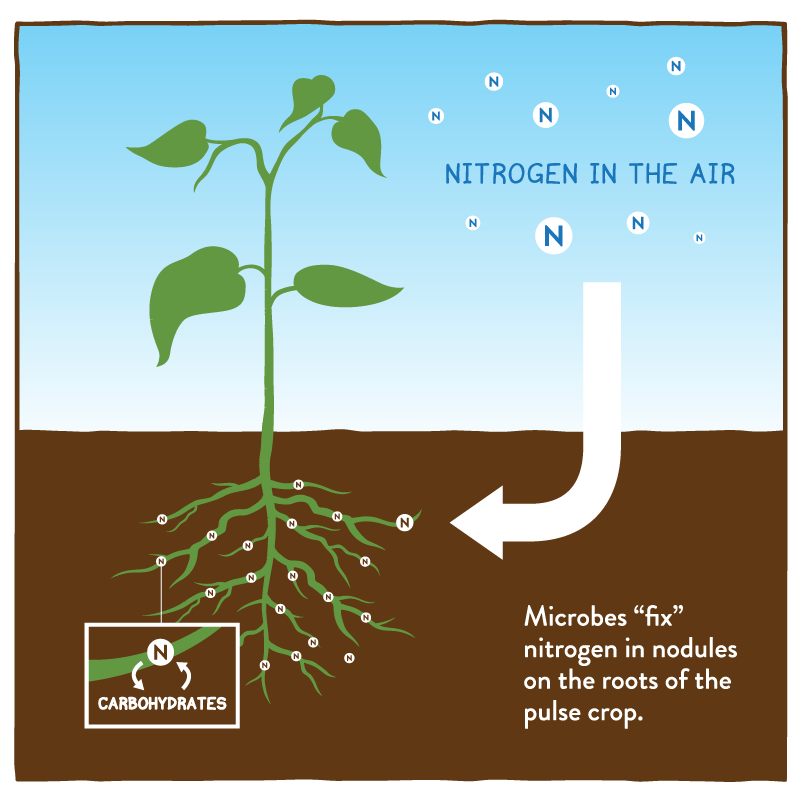
Nitrogen-fixing plants are those whose roots are colonized by certain bacteria that extract nitrogen from the air and convert or “fix” it into a form required for their growth. The symbiotic bacteria, called Rhizobia, form nodules in the root systems, producing nitrogen compounds that help the plant to grow.
Benefits of Using Nitrogen-Fixing Plants or Trees
Environmental Protection: Reduces the need for chemical fertilizers, which can harm ecosystems and water supplies.
Soil Enrichment: Nitrogen-fixing plants increase soil fertility through a symbiotic relationship with bacteria that convert atmospheric nitrogen into a usable form. This added nitrogen also enhances the growth of neighboring plants and improves overall soil health.
Sustainable Agriculture: Promotes eco-friendly farming practices that maintain soil health and productivity over time.
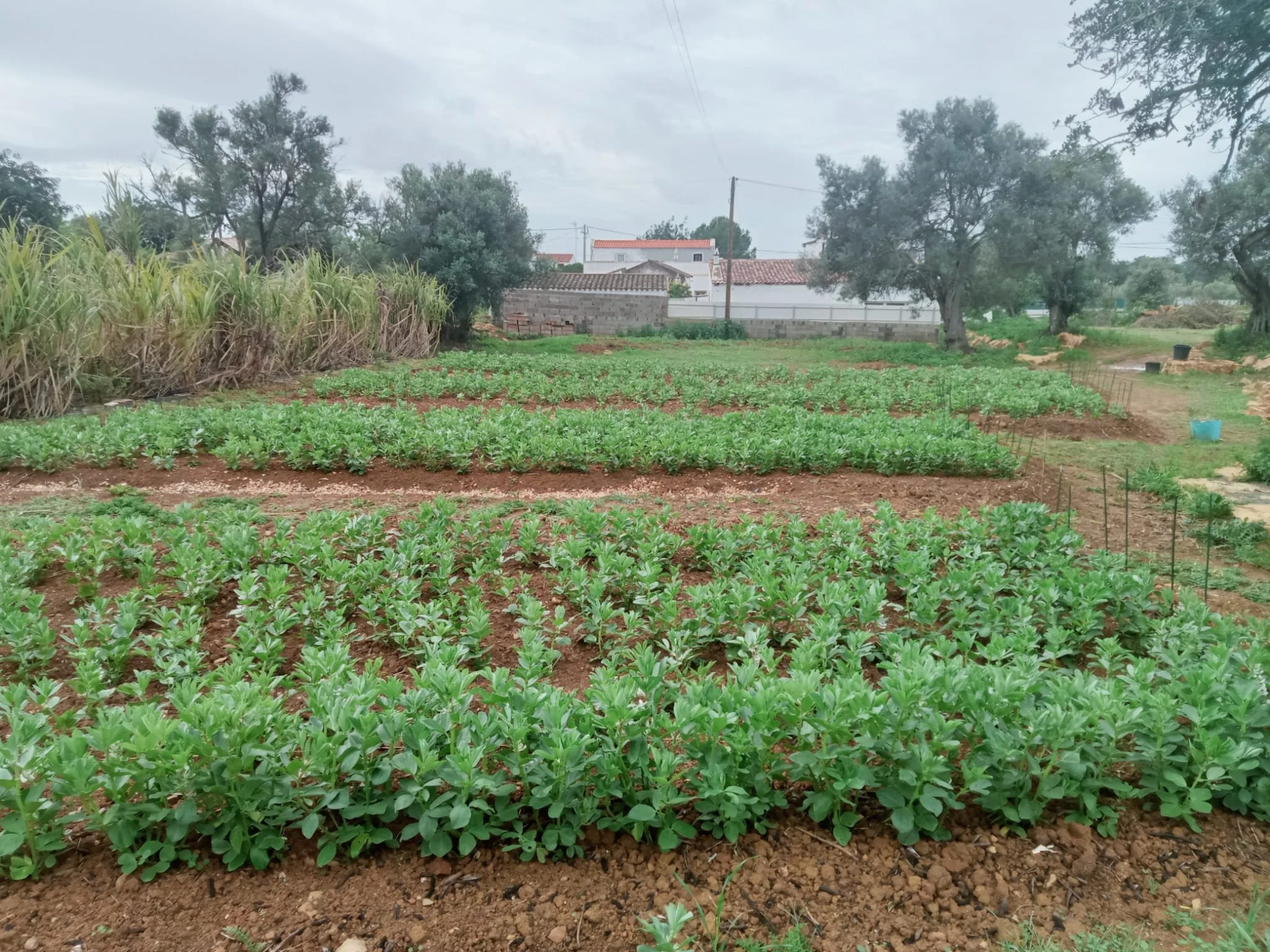
Growing nitrogen-fixing fava beans (Vicia faba) as green fertilizer before planting fruit trees (Dry Orchard Experiment, May 2024)
Incorporating the fava plants into the soil before they flower to maximize nitrogen intake (Dry Orchard Experiment, May 2024)
Maximizing Nitrogen Fixation
For optimal nitrogen fixation, it is recommended to remove flowers or fruits from the plant. This encourages the plant to focus its energy on root and nodule development, enhancing its nitrogen-fixing capabilities.
In case you are using nitrogen-fixing annual plants as "green fertilizer," it is recommended to incorporate them into the soil before they flower.
Popular Types of Edible Nitrogen-Fixers for Home Gardens
The best-known and most common plants that contribute to nitrogen fixation are those in the legume family, Fabaceae. There are also non-leguminous nitrogen-fixing plants, among other interesting edible perennial plants.
Ground cover plants: cowpea, lupine, soybean, clovers, peanut, alfalfa, Austrian winter pea, ... These plants are often used as "green fertilizer" before planting trees.
Food Trees and Shrubs:
Cajanus cajan (Pigeon pea)
Capparis spinosa (Caper bush)
Ceratonia siliqua (Carob tree)
Elaeagnus umbellata (Japanese silverberry)
Eleagnus x ebbingei (Ebbing's silverberry)
Geoffroea decorticans (Chañar)
Glycyrrhiza glabra (Common licorice)
Hippophae rhamnoides (Sea buckthorn)
Inga edulis (Ice-cream bean)
Inga feuilleei (Ice-cream bean)
Inga inicuil (Jinicuil)
Inga sessilis (Inga macaco)
Inga spectabilis (Machete ice-cream bean)
Inga vera (Churimo)
Inga vulpina (Dwarf pink inga)
Lablab purpureus (Hyacinth bean)
Pithecellobium dulce (Tamarindo de Manila)
Saccharum officinarum (Sugarcane)
Sesbania grandiflora (Vegetable hummingbird)
Tamarindus indica (Tamarind)
This article was compiled by Miguel COTTON. If you have any questions or suggestions, do not hesitate to contact us. miguel@orchardofflavours.com